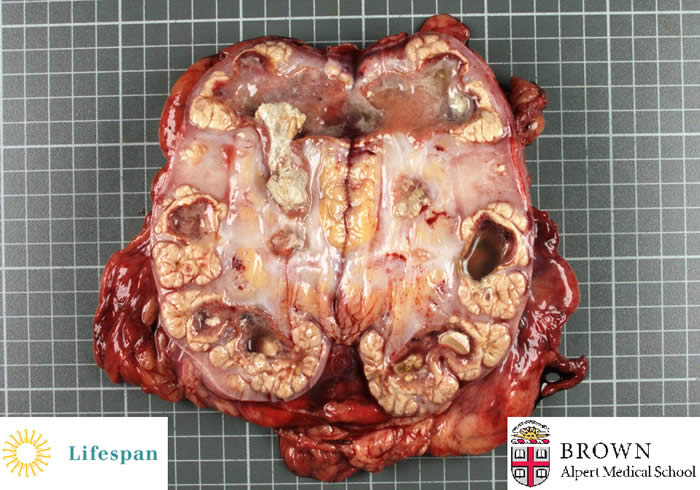
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
A 28 year old female presented with chills, fever and dysuria. CT demonstrated renal calculi and a pigtail stent is placed to improve outflow. Two weeks later the patient returns with nausea and vomiting and is found to have a non-functional kidney which is removed.

Gross photograph demonstrates yellow nodules in the calyceal regions with staghorn calculi occluding the pelvicalyceal system along with copious pus.
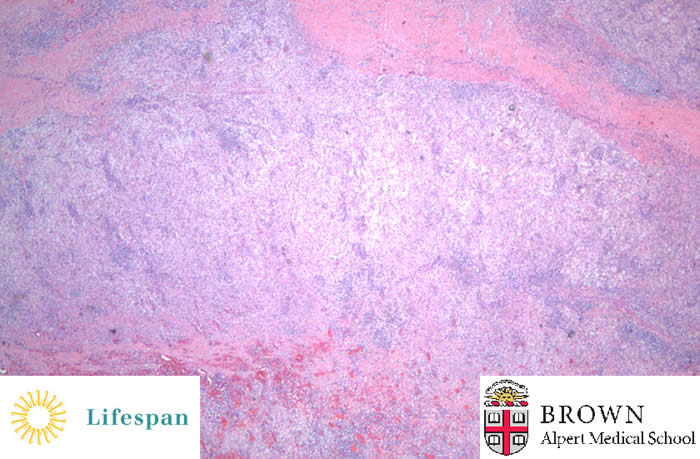
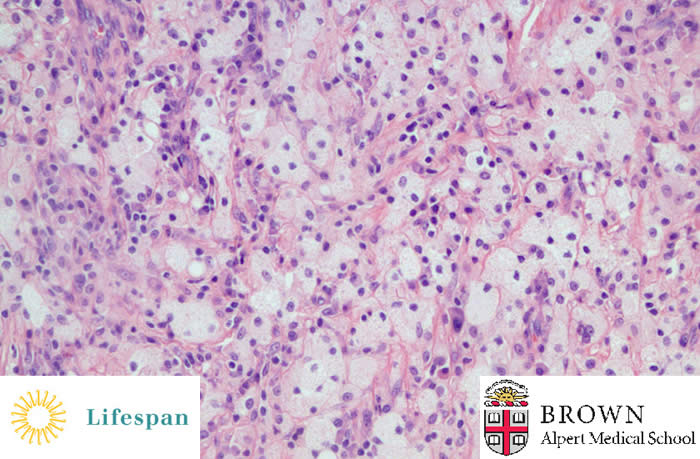
Microscopically, the yellow nodules are comprised of numerous chronic and acute inflammatory cells, the most prominent of which are foamy, lipid laden macrophages. The inflammatory infiltrate completely destroys and replaces the normal renal parenchyma.
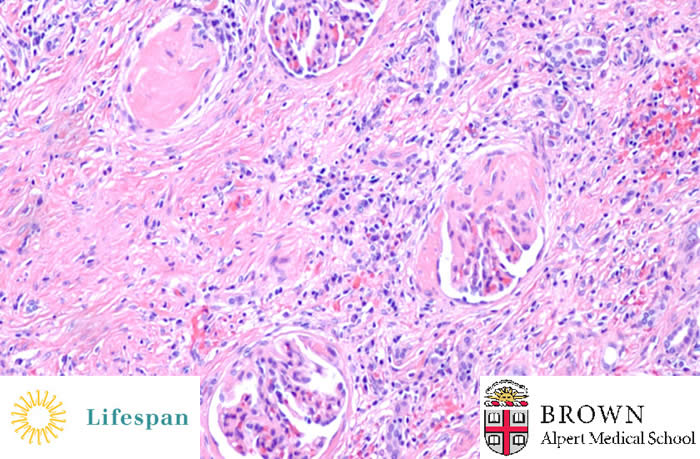
Sclerosed glomeruli are noted along with interstitial inflammation and fibrosis.
This is an uncommon sequelae of pyelonephritis. The differential diagnosis includes clear cell renal cell carcinoma and malakoplakia on gross examination.
Contributed by Sonja Chen, MD