Granulosa Cell Tumor (adult type)
The patient was a 79-year-old female presented with vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain 2 months ago. The endometrial biopsy revealed "infarcted polyp". Pelvic ultrasound showed "2 complex cysts of left ovary". Serum CA-125 was 199 (elevated).

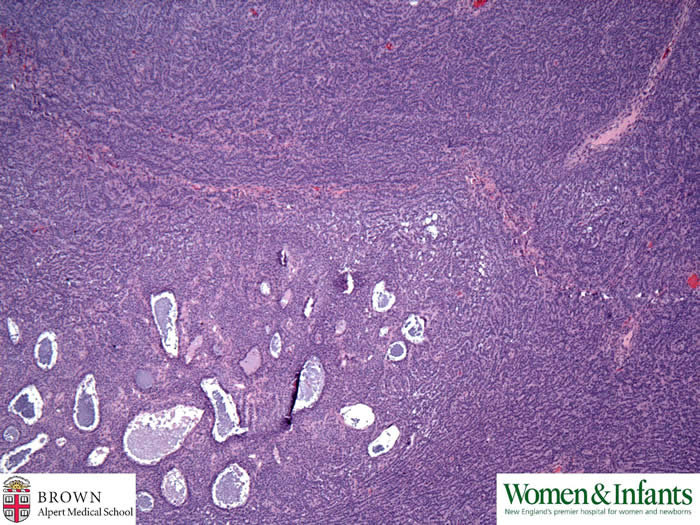
At lower power, the ovarian mass has solid and trabecular patterns. Multiple small follicle-like structures are noted.
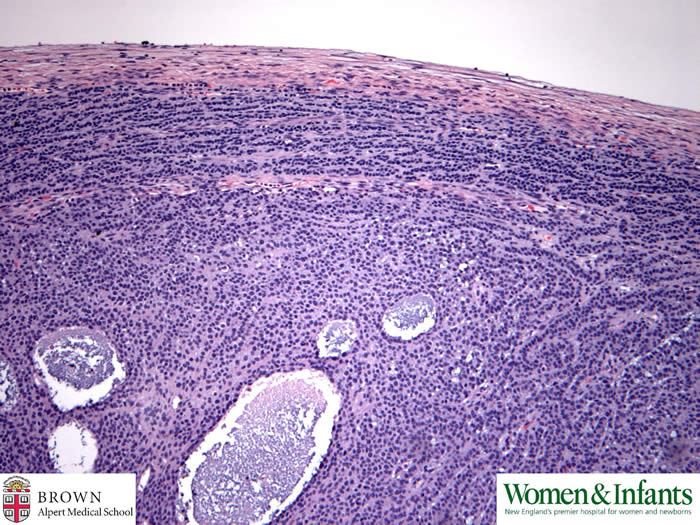
Tumor cells form cord-like pattern in the sub-capsular area.
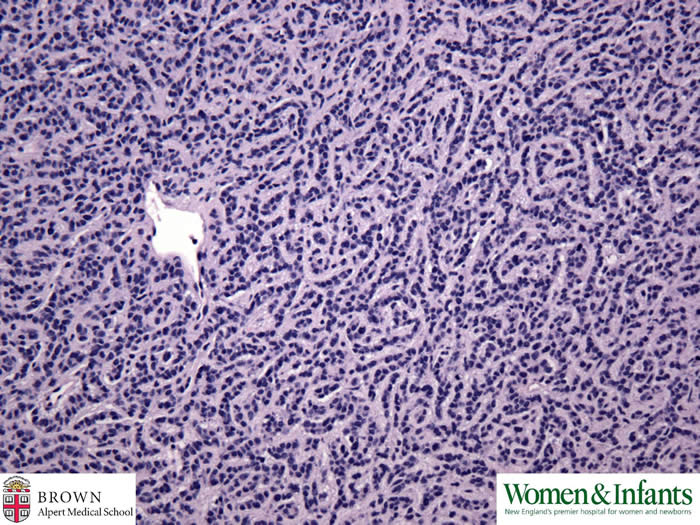
Insular pattern is also present.
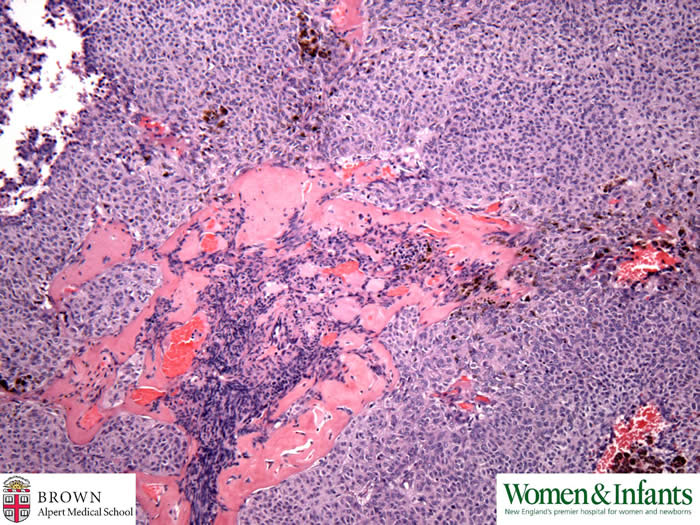
Old hemarrhage and hylinized fibrosis.
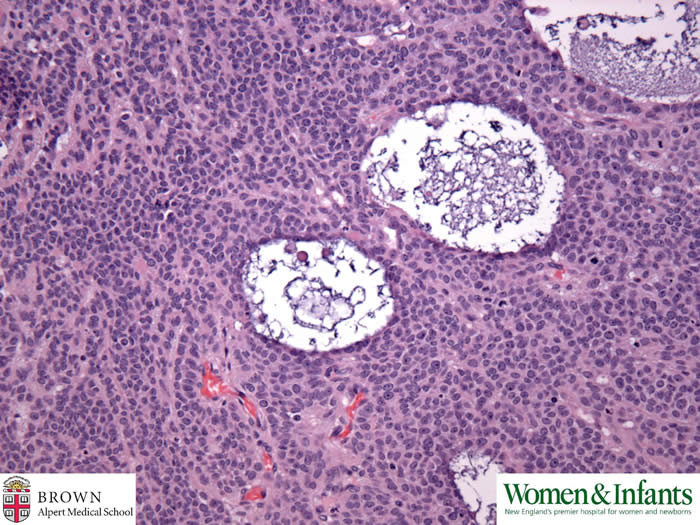
Follicule-like structures contain bead-like acidophilic material that forms zona pellucida in normal follicles.
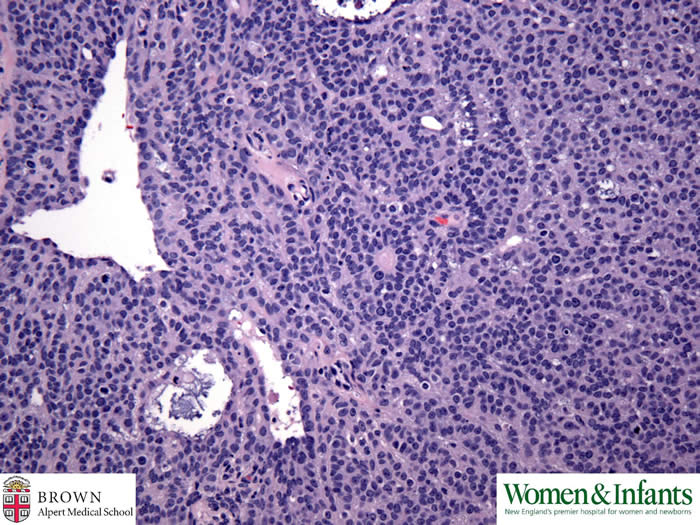
Call-Exner body is formed by layers of closely arranged granulosa cells surrounding the same acidophilic material.
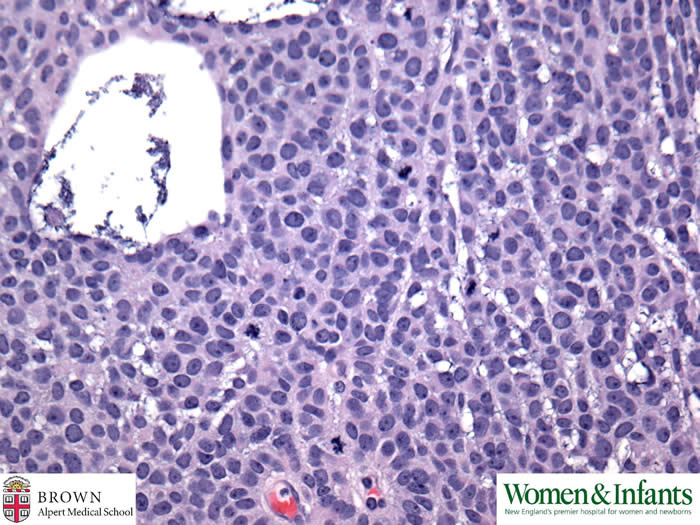
High mitotic activity is locally evident.
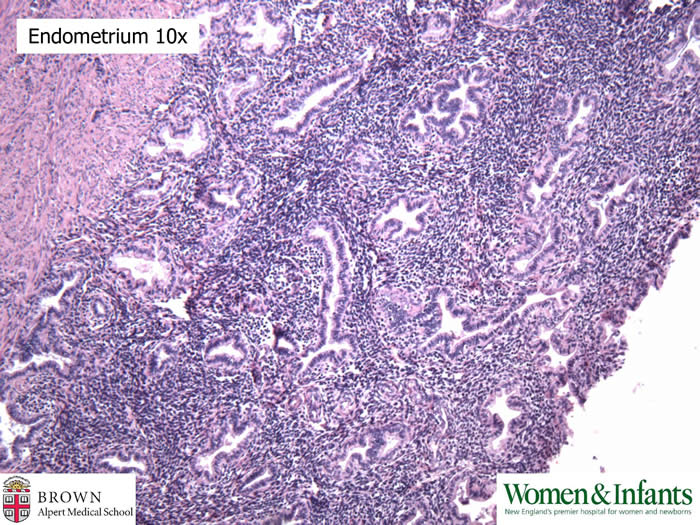
Thickened endometrium is caused by excessive estrogen produced by the tumor.
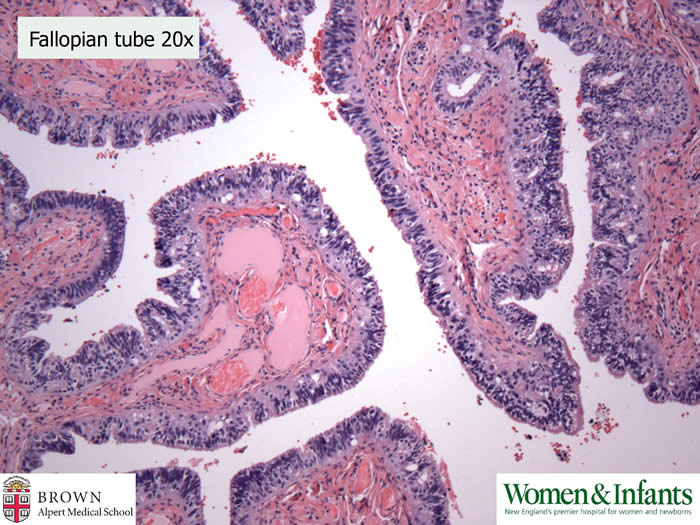
The fallopian tube epithelium is also thickened due to excessive estrogen.
Granulosa cell tumor can be adult type (this case) or juvenile type. The cut-off age is 30 in most cases. Tumor varies in size and can be uniformly solid or uniformly cystic, but most are complex. Solid component appears yellow grossly. Hemorrhage occurs frequently. Tumor cells resemble normal granulosa cells, forming sheets of round or oval cells. Longitudinal nuclear grooves can be very prominent. Other growth patterns include "water-silk" and gyriform, which are uncommon.
Molecular alteration in GCT has recently been elucidated. FOXL2 402C→G missense mutation was "present in 86 of 89 morphologically identified adult-type GCTs (97%)", and "in 1 of 10 juvenile-type GCTs (10%)"( N Engl J Med 2009; 360:2719-2729). FOXL2 "gene encodes a forkhead transcription factor. The protein contains a fork-head DNA-binding domain and may play a role in ovarian development and function. Mutations in this gene are a cause of blepharophimosis syndrome and premature ovarian failure". (http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
The clinical outcome of GCT is usually good. The 10 year survival is greater than 90%. It tends to recur locally. It is one of the cancers that can recur after a long period of time (up to 20 years).
Contributed by Dr. Shaolei Lu and Dr. James C. Sung