Juvenile Granulosa Cell Tumor
An 8 year old girl presented with precocious puberty. Pelvic ultrasound revealed a right ovarian mass.

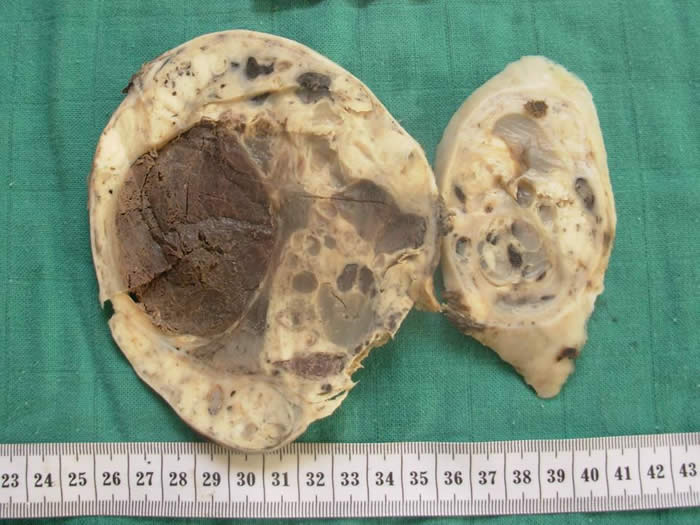
Gross image: 14 x 11 x 4 cm multiloculated, cystic and solid tumor with yellow-white solid areas and necrosis.
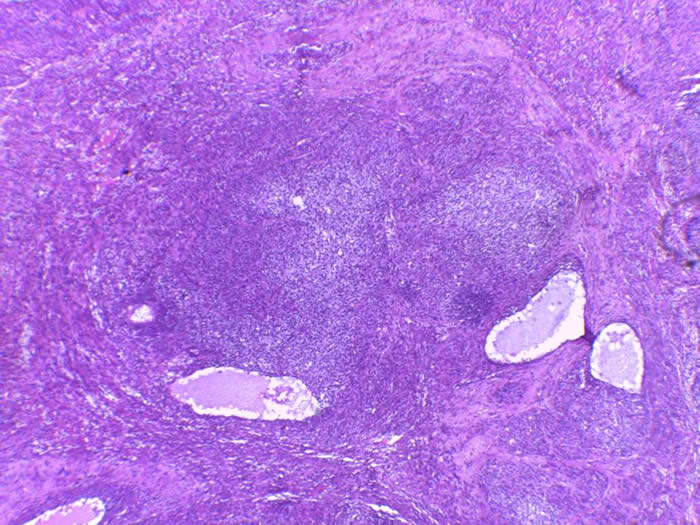
At lower power, At low power, tumor cells arranged in follicules alternating with solid areas.
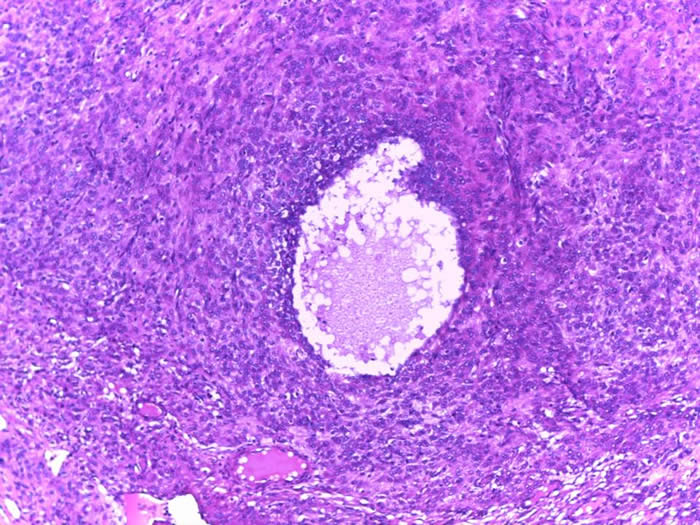
Macrofollicular pattern with cysts containing eosinophilic secretions.
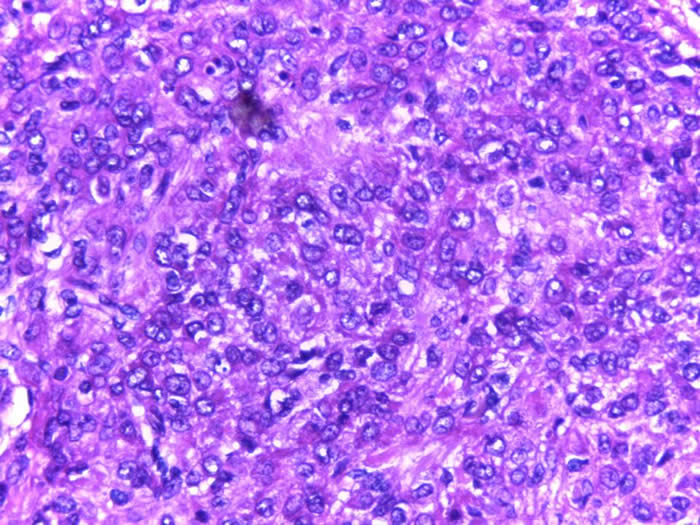
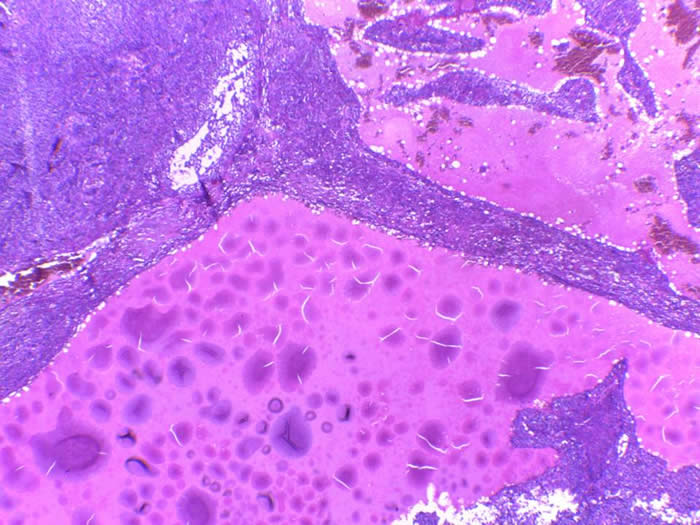
The tumor cells have scant cytoplasm; round or oval hyperchromatic nuclei with small nucleoli and irregular nuclear contours. There is no nuclear grooves.
Among the histologic subtypes of granulosa cell tumors, juvenile granulosa cell tumors are rare, and typically present early. It comprises only 5% of ovarian tumors of childhood or adolescence.
Precocious puberty is common due to excessive estrogen production.
The average size is 12,5 cm. Tumor can be solid and cystic with cysts containing hemorrhagic fluid. The solid areas are yellow-gray and can show extensive necrosis or hemorrhage.
The classic pattern is defined by a solid neoplasm with focal follicle formation. Follicles vary in size and shape with eosinophilic or basophilic secretions staining positive for mucicarmine The cells feature nuclei that are round hyperchromatic and lack the grooves seen in the adult variant. Other features often present include abundant luteinized eosinophilic cytoplasm, high mitotic activity, nuclear atypia and occasionally hobnail-like cells.
Tumoral cells exhibit positivity with Calretinin and inhibin. Alpha-inhibin immunohistochemical staining should be used only when a difficult morphologic diagnosis is encountered.
The differential diagnosis includes adult granulosa cell tumors, thecoma and occasionally clear cell carcinoma
The prognosis is excellent after salpingooophorectomy in patients who have only ovarian involvement.
Contributed by Dr Lamiaa Rouas and Dr Zaitouna Alhamany
Department of Pathology, Mohamed V University School of Medicine, Rabat, Morocco
Correspondance: Lamiaa Rouas; [email protected]