

General Population
There is a range of problems with alcohol and other drugs—hazardous use, unhealthy use, abuse, dependence (or addiction). In the United States the greatest problem with alcohol and other drugs is not dependence. Less than 10% of the U.S. population is dependent on alcohol and/or other drugs while 30% use alcohol at unhealthy levels, placing them at risk for social, legal, and medical problems associated with their use even though they are not dependent (Saitz, 2005). In 2006, 23% of Americans aged 12 or older participated in binge drinking, meaning they drank five or more drinks for men and four for women on the same occasion on at least one day in the past month (SAMHSA, 2007).
Unhealthy levels of alcohol and drug use can lead to hazardous behaviors, such as driving while intoxicated (DWI) by alcohol and/or other drugs.
- 30.5 million people aged 12 or older drove under the influence of alcohol at least once in the past year.
- 10.2 million people aged 12 or older reported driving under the influence of an illicit drug during the past year.
- The rate of driving under the influence of illicit drugs was highest among 18 to 25 year olds
- Almost 50% of patients in trauma centers have positive blood alcohol concentrations.
Illicit drug use includes the use of illegal drugs, like marijuana and heroin, and the inappropriate use of prescription drugs. In 2006, about 20.4 million (8.3%) of Americans aged 12 or older used an illicit drug in the past month. Marijuana is the most commonly used illicit drug and prescription drugs are the second most commonly abused. In 2006, 5.2 million Americans aged 12 or older used prescriptions drugs non-medically in the past month (SAMHSA, 2007).
Research shows that half of all children in the United States live in a household where a parent or other adult uses tobacco, drinks heavily or uses illicit drugs—almost 25% of children live in a household where an adult is a binge or heavy drinker while 12.7% live in a household where a parent or other adult uses illicit drugs (SAMHSA, 2006). Alcohol and other drug use by parents or other adults in the home increases the likelihood that a child will use alcohol and other drugs. In 2006, 15.4% of 12th graders reported using a prescription drug nonmedically within the past year (Johnson et al 2007). Rates of bingeing and heavy drinking are much higher among young adults aged 18-25—in 2006, 42.2% reported binge drinking, and 15.6% reported heavy drinking. Rates of tobacco use are also highest among young adults aged 18 to 25 (SAMHSA, 2007).
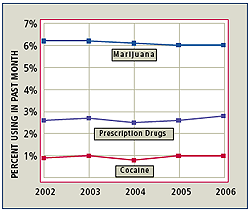
Illicit Drug Use, 2002-2006
This graph is a comparison of past month use of selected illicit drugs among persons ages 12 or older in 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006. The use of marijuana has decreased, but remains the most commonly used illicit drug (Modified from SAMHSA, 2007).









