Laboratory ventilation is an important engineering control measure used to protect laboratory personnel from exposure to hazardous materials used in the laboratory. The chemical exhaust hood is the most useful of these engineering controls. The purpose of a chemical exhaust hood is to prevent or minimize the escape of airborne contaminants from the hood to the laboratory air.
Hood performance and efficiency depends on an adequate and uniform velocity of air moving through the sash opening. Hood performance is adversely affected by many factors including mechanical malfunction, drafts or open doors and windows, and poor operating procedures of the person using the hood.
Description of a Chemical Exhaust Hood
A fume hood is a ventilated enclosure used to control exposure to hazardous or odorous chemicals. An exhaust fan draws air into the front opening of the hood, then up and out of the hood through the ductwork. Because the air that is pulled into the hood is not filtered, fume hoods only offer protection to its users and no protection to the products inside the hood.
A properly operating and correctly used fume hood will protect workers by containing vapors, dusts, gases, and mists. The sash can also act as a shield to workers from splashes and minor explosions or fires that may occur inside the hood. A fume hood is not designed to protect the skin or hands of workers placed inside the fume hood during activities. Personal Protective equipment (eye protection, gloves and lab coat) must be used to protect the skin that is exposed to the open area of the fume hood.
Fume hoods are the primary engineering controls used to control inhalation exposures to hazardous substances in University research buildings. There are other types of local exhaust such as vented enclosures for large pieces of equipment or chemical storage, and snorkel and canopies for capturing contaminants near the point of release. Work is performed directly underneath the canopy or snorkel and is typically intended for machines such as gas chromatographs or mass spectrometers. This type of local exhaust does not guarantee 100% removal of gases.
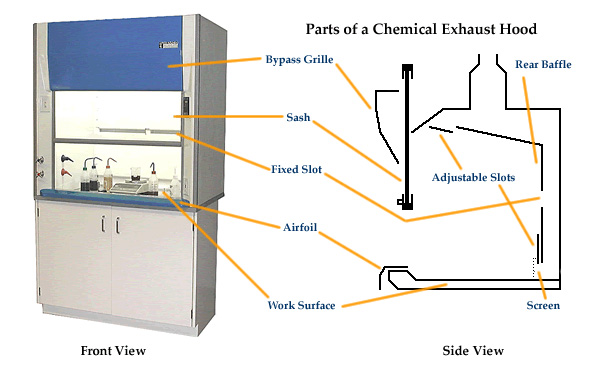
| Bypass Grille | produces additional air that varies with the sash height; keeps face velocity |
| Sash | sliding "door" to the hood, adjusts amount of airflow into the hood |
| Fixed Slot | helps to distribute airflow evenly across the hood face |
| Airfoil | streamlines airflow into the hood, preventing eddies that carry vapors out of the hood |
| Work Surface | hood surface, usually recessed to contain spills within the hood |
| Rear Baffle | moveable partition used to create uniform airflow across the hood opening |
| Adjustable Slots | moveable slots used to create uniform airflow across the hood opening |
| Screen | prevents materials from blocking uniform airflow across the hood opening |
Ductless Hoods and Hood Modifications
Ductless hoods are hoods that are not connected to external ductwork. The air that enters into the hood is filtered and then returned directly to the lab. This type of hood is not used for volatile or hazardous chemicals. Ductless hoods are prohibited at the University unless specifically approved by the EHS Director, Chemical Hygiene Officer, and Facilities Management.
Modifications to hoods or ductwork by researchers are strictly prohibited. Please contact Facilities Management at 401-863-7800 or EHS at 401-863-3353 if a modification needs to be made. It is University policy that any changes made to local exhaust systems must be approved by EHS staff and Facilities Management. The cost for performance testing or repairs on fume hoods that have unauthorized modifications will be the responsibility of the Laboratory Supervisor or Department.
Do not use a fume hood for large pieces of equipment unless you intend to dedicate the fume hood for this use, since it may cause excessive air turbulence, variations in face of velocity, and loss of containment. It is generally more effective to install a specially designed enclosure for large equipment so the fume hood can be used for its intended purpose.
Fume Hood Decontamination
Fume hoods used for work with chemicals, biologicals, or radioactive materials must be decontaminated and washed before being repaired, moved, or discarded. Decontamination methods will depend on the materials used inside the hood.
